19.3 Viroids, viruses, and prions are formidable pathogens in animals and plants
Viral disease in Animals: Symptoms may be caused by direct harm to cells or by the body's immune response. Vaccines stimulate the immune system to defend the host against specific viruses.
Emerging viruses: Outbreaks of "new" viral diseases in humans are usually caused by existing viruses that expand their host territory . The H5N1 avian flu virus is being closely monitored for its potential to cause a serious flu pandemic.

Viral diseases in plants: Viruses enter plant cells through damaged cell walls (horizontal transmission) or are inherited from a parent (vertical transmission).

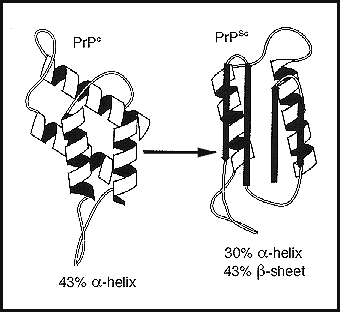
Viroids and prions: The simplest infectious agents. Viroids are naked RNA molecules that infect plants and disrupt their growth. Prions are slow-acting, virtually indestructable infectious proteins that cause the brain diseases in animals.
Prions are misfolded proteins that cause the misfolding of normal proteins when they come into contact with one another. Prions are infectious proteins.
CHAPTER 20: Biotechnology
DNA cloning yields multiple copies of a gene or other DNA segment.
Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been artificially made, using DNA from different sources anf often different species. An example is the introduction of a human gene into an E. coli bacterium.

Biotechnology is the process of manipulating organisms for the purpose of making products for the public.
Genetic engineering is the process of manipulating genes and genomes.
Gene cloning is the process by which scientists can create significant sample of specific segments of DNA that they can then manipulate in the lab.
link to gene cloning video: http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.upload.eg123.com/uploads/2f10bae678.jpg&imgrefurl=http://pharma2010.wordpress.com/2008/01/21/animation-to-genetic-1/%3Freferer%3Dsphere_related_content/&usg=__u8cXPen22F901Gj0--tkH8ZLlM8=&h=417&w=501&sz=27&hl=en&start=3&sig2=60IMxZQ9OYfvUIelSFOJRg&um=1&tbnid=Y8QQdCAjrU7_3M:&tbnh=108&tbnw=130&ei=oVWCSeIahpaxA83l9coN&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dvideo%2Bgene%2Bcloning%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26safe%3Doff%26client%3Dfirefox-a%26rls%3Dorg.mozilla:en-US:official%26sa%3DN
When a DNA molecule is cut by restriction enzymes the result will always be a set of restriction fragments which will have at least one single-stranded end, called a sticky-end. Sticky ends can hydrogen bond with complementary single-stranded pieces of DNA, and these unions can be sealed with an enzyme called a DNA ligase.
The Cloning of genes generally occurs in five steps:
First the vector and the gene mist both be isolated. The vecter and the gene must both be isolated. The vecter is the plasmid (usually bacterial) that will carry the DNA sequence to be cloned.
The DNA in question must be inserted into the vector (plasmid).
The vector must be inserted into the cell in order to be copied.
The cells must be cloned.
The cells carrying the clones myst be identified and isolated.
A genomic library is a collection of many bacterial or phage clones. Each clone carries copies of a particular DNA segment from a foreign genome, integrated into an appropriate DNA vector, such as a plasmid or a trimmed-down phage genome. In a complete genomic library, the foreign DNA segments cover the entire genome of an organism.
PCR require double-stranded DNA containing the target sequence, a heat-resistant DNA polymerase, all four nuclotides, and two 15 to 20 nucleotide DNA strands that serve as primers. One primer is complementary to one end of the target sequence on one strand, the second primer is complimentary to the other enf of the sequence on the other strand.
DNA technology allows is to study the sequence, expression, and function of a gene.
Gel eletrophoresis is a lab technique that is used to seperate macromolecules on the basis of their size and charge by using an electric current.
Southern blotting is a technique that is used to determine the presence of specific nucleotide sequences in DNA.
Cloning organisms may lead to production of stem cells for research and other applications.
Animal stem cells, which can be isolated from early embryos or adult tissues and grown in culture, are self-perptuating, relatively undifferentialted cells. Embryonic stem cells are easier to grow than adult stem cells and can theoretically give rise to all types of cells in an organism. The range of cell types that can arise from adult stem cells is not yet fully understood.
Multiple Choice
1. To cause a human pandemic, the H5N1 avian flu virus would have to
a. spread to primatesb. develop into a virus with a different host range
c. become capable of human-to-human transmission
d. arise independently in chickens
e. become much more pathogenic
2. Which of the following do both viruses and bacteria have in common?
a. metabolism
b. ribosomes
c. genetic material made of nucleic acid
d. cell division
e. independent existence
3. Which of the following are not emerging viruses?
a. AIDS
b. SARS
c. HIV
d. Ebola virus
e. Malaria
4. When an animal is cloned what is removed from the egg cell donor?
a. mRNA
b. rRNA
c. DNA
d. nucleus
e. mitochondria
5. True or False. Embryonic stem cells are easier to grow than adult stem cells
answers: 1. c, 2. c, 3. e, 4. d, 5. True
No comments:
Post a Comment